During the week of June 2nd, our science class has been building bottle rockets out of two-liter soda bottles, duct tape, card stock, and cardboard. We had about two hours. We (Killer Science) created a bottle rocket that traveled 76 meters (almost 250 feet). Here's how to make one yourself.
Materials:
- one empty two-liter soda bottle
- one roll of duct tape (any color works)
- one sheet of card stock
- a plastic bag w/ 100 grams of sand inside
- 500 ml of water
- scissors
Procedure:
1.) Cut out three 3 in. by 4 in. by 5 in. right triangles out of cardboard
2.) Cut out three 6 in. by 7 in. by 8.5 in. right triangles out of cardboard
3.) Tape the smaller triangles about 3 in. from the top (the end that you don't normally drink out of) of your two-liter bottle . Space them equally around the bottle, then use the duct tape to secure them. Make sure that the wings are secure or else they will fall off during the launch.
4.) Tape the larger triangles 6 in. from the top (the end you don't normally drink out of) of your bottle, between the smaller triangles. Again, make sure to secure the wings.
5.) Use the card stock to create a circle with a 4 in. radius. Using a compass is best, but freehand works, too. Then, cut from the outer edge of the circle directly to the center. Fold it into a cone shape.
6.) Put the plastic bag w/ 100 grams of sand inside your cone and duct tape it to what will be the front of your rocket.
7.) Duct tape over any rough edges or folds of tape to reduce wind resistance during flight. This will slow down the rocket, and it will not travel as far.
8.) Pour the 500 ml of water into your rocket. You may want to use a funnel to help prevent spilling.
Note: It is incredibly important that during the process of building your rocket that you do not damage or puncture it. Your rocket will not be able to build up pressure and therefore will not fly if this happens.
Friday, June 6, 2014
Monday, June 2, 2014
The Rules Of The Solar System and The Galaxy
Solar Nebula Theory- The solar nebula theory states that the solar system came to be when a star exploded and formed a rotating nebula that from which the sun and planets were formed.
- Newton’s Three Laws-
1)The law of inertia-An object at rest will stay at rest and an object in motion will stay in motion until acted upon by an unbalanced force
2)F=ma
3)Every action has an equal and opposite reaction
- Kepler’s Three Laws-
1)The Law of Ellipses-Planets orbit the sun in an ellipse
2)The Law of equal areas-speed at which any planet moves through space is constantly changing. A planet moves faster when it is closer to the sun
3)The Law of Harmonies-compares the orbital period and radius of orbit of a planet to those of other planets. Orbital period squared over the average distance from the sun cubed is the same for every planet
- How Fast you are moving when you are sitting still
Universe-stretches-gamma-rays expand to x-rays to ultra-violet light to visible light to micro and radio waves.
Galaxy-spinning- thought to be orbiting the universe and moving through space towards The Great Attractor at 1.3 million miles per hour
Sun and therefore the solar system- milling around or orbiting the center of the galaxy at 483000 miles per hour. 225 million years per orbit
Earth-spinning at 1000 miles per hours and revolving around the sun at 66000 miles per hour
Explain the rules that govern or solar system and galaxy
Friday, May 16, 2014
The Quest for the Proper Insulation
Once upon a time in a kingdom where all the subjects were science bloggers, there was a house in desperate need of an energy audit and an organization called the Red Cross in need of an insulated bottle to carry cold liquid.
One day the citizens decided to help the homeowner of the house and deduce what was wrong with the house. They started by walking leagues around the house and finding cracks in the foundation, vents leading from the basement and attic to the outside kingdom, plywood floors under the laundry room, and holes in the roof. When they ventured in the back door what they found was much worse, 60 watt light bulbs, cracks in the dining rooms wooden beams and cracks in the stairs letting air in from the basement, a disastrous fireplace mantle and air ventilation system as well as lacking insulation. Many of these observations were found using a contraption called a blower door that essentially sucks the air from the house so you can feel where the air comes in the house from. After completing a packet and identifying the problems with the house brave bloggers entered the basement to find the source of many problems. The basement was a scene from a horror movie with cobwebs and heat ducts spreading every which way. All the heating ducts were unsealed and their metal bodies were open to the unforgivable cold of the basement. Once the bloggers wrote a letter to the house’s homeowner explaining their findings and recommendations to fix the problems they focused their combined attention on other matters.
In order to test their findings, the bloggers decided to create a portable insulation system, or a “thermos.” This “thermos” was to be sent to the Red Cross Organization, in order to save refugees from a terrible death known as dehydration. The bloggers set out on a quest to save refugees. First, they came up with a plan. Their plan included a large bottle, some recycled paper, bubble wrap, and duct tape… colorful duct tape. The bloggers then pieced the objects together to create their masterpiece. First, they put the recycled paper, known as cellulose, into the bottom of the large bottle. Then, they bubble-wrapped a normal sized bottle, and packed some more cellulose around it. Finally, they duct taped more bubble wrap onto the top of the bottle. At last, the bloggers had finished their creation. This masterpiece was durable, and only lost 1.5 degrees Celsius every 30 . Their cold water bottle would stay cold, and the refugees were saved!
Sunday, April 20, 2014
Earth: Plate Tectonics
Recently we have started the plate tectonics unit of Earth Science. Alfred Wegener was the first to propose continental drift. He cited coastlines and fossils as clues that all the continents once fit together like a puzzle in a supercontinent called Pangea. The coastlines of south america and africa were two pieces in the puzzle. He found fossils of the freshwater Mesosaurus on south america and Africa, as well as fossils of the Glossopteris fern. He, however proposed that the continents movement was due to them floating on the ocean.
The Theory of Plate Tectonics states that the lithosphere is broken into pieces, called plates, that “float” on the asthenosphere and “move” due to convection (figure 1). 
Convection is the motion of heat moving outwards from the earth’s core moving material upwards with it and then cooling and sinking towards the core (figure 2). 
The lithosphere is less dense and more rigid than the asthenosphere which is liquid. This is why the lithosphere “floats” on top of the asthenosphere.
Evidence to support this theory includes earthquakes, volcanoes, surface features such as mountains, mid-ocean ridges, and rift valleys, Wegener’s evidence, ocean crusts, and magnetic stripping. Earthquakes and volcanoes occur because of plate movement (figure 3). 
The oceanic crusts contain evidence of plate movement because near spreading ridges material rises due to convection creating new oceanic crust and pushing the existing crust aside (figure 4). 
Magnetic striping is identifying the alignment of iron molecules with the magnetic field. The ocean floor records Earth’s magnetic history. In the past the direction of the molecules flip indicating that the Earth’s magnetic field has flipped since its origin (figure 5).
There are three types of plate boundaries. Transform boundaries, convergent boundaries, and divergent boundaries. Transform boundaries are created when two plates move along each other in opposite directions (figure 6).
A convergent boundary is where two plates are moving away towards each other. If the two plates are oceanic or one continental and one oceanic then one oceanic plate will sink below the other plate.If the two plates are continental then they create mountains as both have equal density.These boundaries can cause mountains to form such as the Himalayas (figure 7).
A divergent plate boundary is where two plates are moving away from each other (figure 8).
An example of plate tectonics is the 2011 Japan Tsunami. The devastating tsunami that wiped out many lives in Japan was caused by the largest fault slip recorded. The magnitude 9 earthquake occurred along the Japan trench. Unlike other high magnitude earthquakes, which usually slip around 20-25 meters, but the 2011 quake slipped about 50 meters. This movement was enough to force up water and cause a devastating tsunami.
The friction of rock-on-rock movement would not have allowed such a large slip, so a lubricator such as clay must have been present. Clay is an incredibly slippery substance, so it encourages large slips at plate boundaries. The clay coating on the plate helped reduce the heat and friction produced by the sudden slip. The severity of the earthquake, and therefore the tsunami, are at fault of the clay. (Lee 2013)
Lee, Jane J. "The 2011 Japan Tsunami Was Caused By Largest Fault Slip Ever Recorded." National Geographic. National Geographic Society, 05 Dec. 2013. Web. 20 Apr. 2014.
Thursday, April 17, 2014
Earth's History: Summary
Recently we have started the plate tectonics unit of Earth Science. Alfred Wegener was the first to propose continental drift. He cited coastlines and fossils as clues that all the continents once fit together like a puzzle in a supercontinent called Pangea. The coastlines of South America and Africa were two pieces in the puzzle. He found fossils of the freshwater Mesosaurus on south america and Africa, as well as fossils of the Glossopteris fern. He, however proposed that the continents movement was due to them floating on the ocean.
The Theory of Plate Tectonics states that the lithosphere is broken into pieces, called plates, that “float” on the asthenosphere and “move” due to convection (figure 1). 
Convection is the motion of heat moving outwards from the earth’s core moving material upwards with it and then cooling and sinking towards the core (figure 2). 
The lithosphere is less dense and more rigid than the asthenosphere which is liquid. This is why the lithosphere “floats” on top of the asthenosphere.
Evidence to support this theory includes earthquakes, volcanoes, surface features such as mountains, mid-ocean ridges, and rift valleys, Wegener’s evidence, ocean crusts, and magnetic stripping. Earthquakes and volcanoes occur because of plate movement (figure 3). 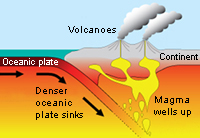
The oceanic crusts contain evidence of plate movement because near spreading ridges material rises due to convection creating new oceanic crust and pushing the existing crust aside (figure 4). 
Magnetic striping is identifying the alignment of iron molecules with the magnetic field. The ocean floor records Earth’s magnetic history. In the past the direction of the molecules flip indicating that the Earth’s magnetic field has flipped since its origin (figure 5).
There are three types of plate boundaries. Transform boundaries, convergent boundaries, and divergent boundaries. Transform boundaries are created when two plates move along each other in opposite directions (figure 6).
A convergent boundary is where two plates are moving away towards each other. If the two plates are oceanic or one continental and one oceanic then one oceanic plate will sink below the other plate.If the two plates are continental then they create mountains as both have equal density.These boundaries can cause mountains to form such as the Himalayas (figure 7).
A divergent plate boundary is where two plates are moving away from each other (figure 8).
The devastating tsunami that wiped out many lives in Japan was caused by the largest fault slip recorded. The magnitude 9 earthquake occurred along the Japan trench. Unlike other high magnitude earthquakes, which usually slip around 20-25 meters, but the 2011 quake slipped about 50 meters. This movement was enough to force up water and cause a devastating tsunami.
The friction of rock-on-rock movement would not have allowed such a large slip, so a lubricator such as clay must have been present. Clay is an incredibly slippery substance, so it encourages large slips at plate boundaries. The clay coating on the plate helped reduce the heat and friction produced by the sudden slip. The severity of the earthquake, and therefore the tsunami, are at fault of the clay. (Lee 2013)
Figure 8-http://serc.carleton.edu/images/eet/seismicwave/spreading_center.gif
Monday, March 24, 2014
Nuclear Fusion: Opinion: ITER
Money management and finances for ITER are so complicated that it needs its own currency. This is known as the ITER Unit of Account. Despite its cost and complexity, ITER will be a solution to the energy crisis.
In our opinion the investment of billions of dollars for ITER will be worth the cost. ITER will solve the worlds energy problems for the next 30 million years, a major return for the investment. In the near future the availability of fossil fuels will decline and if we do not find alternative energy sources the world will go into an energy crisis. Nuclear fusion is an option in alternative energy resources. The ITER proposes little danger to the world and will run on no more than seaweed and lithium.
Overall, the ITER is an investment that will pay off for 30 million years, and "will benefit everyone by providing, clean,near limitless energy" (West, 2014).
Saturday, March 22, 2014
Nuclear Fusion: Future or Fantasy?
As we use energy, we use resources. Eventually, resources such as coal and oil will run out.
What will we do then?
Through fusion, we can create electricity. Fusion is safe, but very tricky to do. In nuclear fusion, two isotopes such as deuterium and tritium will combine to create Helium-5. Helium is not an element that likes to hang on to extra neutrons, so it gets rid of it almost immediately. The discharge of helium's extra neutron creates a massive amount of energy.
 In about a decade, the most complex machine ever built will be turned on. This massive machine is known as the International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor, or ITER. We are going to bottle a star.
In about a decade, the most complex machine ever built will be turned on. This massive machine is known as the International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor, or ITER. We are going to bottle a star.
 ITER will be the hottest thing on the Earth's surface. The many particles whizzing around inside ITER will be contained by a sort of "magnetic bottle". Of course, ITER doesn't come cheap. The whole machine will take billions of dollars to create. It will become the most expensive scientific instrument.
ITER will be the hottest thing on the Earth's surface. The many particles whizzing around inside ITER will be contained by a sort of "magnetic bottle". Of course, ITER doesn't come cheap. The whole machine will take billions of dollars to create. It will become the most expensive scientific instrument.
(both images came from ITER - the way to new energy. (n.d.). Retrieved from https://www.iter.org/sci/whatisfusion)
What will we do then?
Through fusion, we can create electricity. Fusion is safe, but very tricky to do. In nuclear fusion, two isotopes such as deuterium and tritium will combine to create Helium-5. Helium is not an element that likes to hang on to extra neutrons, so it gets rid of it almost immediately. The discharge of helium's extra neutron creates a massive amount of energy.


(both images came from ITER - the way to new energy. (n.d.). Retrieved from https://www.iter.org/sci/whatisfusion)
Wednesday, March 12, 2014
Sodium and Water EXPLOSION!
Today in Honors Earth Science:
This is 2NaOH. There are obviously more than 2 sodium atoms. The water doesn't actually turn pink right after the reaction. The coloring was caused by a universal indicator-type solution. It's still pretty awesome.
Monday, March 10, 2014
Experiment: Mixture Seperation
Objective: To separate a mixture of sand, salt, and iron.
Materials:
- Mixture of sand, salt, and iron
- Magnet
- Plastic bag
- coffee filters
- water
- Paper
- Lab materials (beakers, stirrers, hot plates, funnels, etc)
Procedure:
- Arrange materials
- Calculate the mass of the mixture
- Remove the iron
- Wrap the magnet with the plastic bag
- Put the wrapped magnet in to the three substance mixture
- Remove the magnet from the bag over a piece of paper
- Repeat step 3a-b until there is no more iron in the mixture
- Remove the sand
- Mix the two substance mixture with water
- Using the coffee filter, placed in a funnel, placed in a beaker, filter the sand from the salt-water
- Remove the salt
- Using the hot plate evaporate the water off the salt
- Calculate the mass of each individual substance
- Compare masses of the individual substances to the total mass of the mixture
Analysis:
Mixture- 14.15g
Iron- 6.45g
Sand- 3.8g
Salt- 3.9g
Sunday, March 9, 2014
Experiment: Murder: A forensics lab
On March 6th at 3 am, an assistant baker at Mike’s Awesome bakery in Francestown, NH was found dead lying in a pool of blood. The assistant baker was found covered in a mysterious white powder in which the earth science class must identify.
Investigators collected samples of white powder they found in the bakery (baking soda, baking powder, flour, cornstarch, and the unknown substance found on the body.
As well as collecting substance samples, the investigators interviewed employees of the bakery and took clothing samples to see if any employee had traces of the substance on their person.
Materials:
- baking soda
- baking powder
- flour
- cornstarch
- unknown
- vinegar
- iodine solution
- universal indicator
- water
- lab materials (beakers, stirrers, pipettes, etc)
Objective:
Identify the unknown white powder found on the assistant baker.
Procedure:
- Arrange materials
- Test powders reaction with water
- squeeze 3 drops of water into each substance
- study and record the reaction
- compare substances reactions
- Test powders reaction with vinegar
- Repeat step 2 using vinegar
- Test powders reaction with iodine
- Repeat step 2 using iodine
- Test the powders pH
- Repeat step 2 using the universal indicator
- Clean up materials
- Analyze collected data
- Finalize conclusion and complete lab sheet
Test Solutions
|
Baking Soda
|
Baking Powder
|
Flour
|
Cornstarch
|
Unknown
|
Water
|
- no reaction
|
- mildly fizzy
- mixes with water
|
- slightly sticky
- runs off
|
- changes texture
- Oobleck
- consumption
|
- mildly fizzy
|
Vinegar
|
- fizzes
|
- fizzes
|
- no reaction
|
- no reaction
|
- fizzes
|
Iodine
|
- no reaction
|
- purple/indigo
- bubbles/fizzes
|
- grayish/purple
|
- indigo/red
|
- purple/indigo
-bubbles/fizzes
|
Indicator
|
- teal
- more basic
|
- orange-yellow
- more acidic
|
- orange
-more acidic
|
- red-orange
- more acidic
|
- orange-yellow
- more acidic
|
Conclusion:
The investigators should be looking for baking soda on the suspects clothing. The unknown substances pH was the same as baking soda. The reaction of the unknown with water and the iodine solution is unique in baking soda. Before starting the experiment you could rule out many substance based on their appearance and texture when compared with the unknown. Therefore, I can conclude that the unknown substance is baking soda and the investigators should be looking for traces of it on the suspects clothing.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)


